Introduction:
Digestive discomfort can be a common issue for many individuals, whether due to gastrointestinal conditions, food sensitivities, or simply a sensitive stomach. Choosing foods that are gentle on the digestive system can help alleviate discomfort and promote better digestion. In this article, we’ll explore five food groups that are easy to digest and can be incorporated into a gentle-on-the-stomach diet to support digestive health and overall well-being.
1. Cooked Vegetables
Cooked vegetables are a cornerstone of healthy eating, offering a plethora of nutrients, flavors, and culinary possibilities. From tender steamed broccoli to caramelized roasted sweet potatoes, cooking vegetables transforms them into versatile and delicious additions to any meal.
The process of cooking vegetables involves applying heat to break down their cell walls, making nutrients more accessible and enhancing digestibility. This makes cooked vegetables an excellent choice for individuals with sensitive digestive systems or those seeking to maximize nutrient absorption.
One of the key advantages of cooking vegetables is the preservation of essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. While some nutrients may be lost during cooking, others become more bioavailable, ensuring that cooked vegetables remain a nutrient-rich component of a balanced diet.
Cooked vegetables offer a wide array of health benefits. They are rich in vitamins such as vitamin C, vitamin K, and folate, as well as minerals like potassium and magnesium. Additionally, they provide dietary fiber, which supports digestive health, regulates blood sugar levels, and promotes satiety.
Another advantage of cooked vegetables is their versatility. They can be prepared using various cooking methods, including steaming, boiling, roasting, sautéing, and grilling, each imparting unique flavors and textures. Cooked vegetables can be seasoned with herbs, spices, and sauces to enhance their taste and complement other ingredients in a dish.
In addition to their nutritional value and versatility, cooked vegetables are also convenient. They can be batch-cooked in advance and stored in the refrigerator or freezer for quick and easy meal preparation. Incorporating cooked vegetables into meals is a simple yet effective way to boost the nutritional content of your diet and add color, flavor, and texture to your plate.
Whether served as a side dish, incorporated into soups, salads, or main courses, cooked vegetables are a delicious and nutritious addition to any meal. By experimenting with different cooking methods and flavor combinations, you can discover new ways to enjoy the vibrant flavors and health benefits of cooked vegetables in your diet.
2. Lean Proteins
Lean proteins are an essential component of a healthy diet, providing vital nutrients and supporting various bodily functions. Unlike fatty cuts of meat or processed protein sources, lean proteins offer a lower fat content while still delivering ample amounts of high-quality protein, making them an excellent choice for those looking to maintain a healthy weight, support muscle growth, and improve overall health.
Lean proteins come from a variety of sources, including animal and plant-based options. Animal-based lean proteins include poultry without the skin, such as chicken and turkey breast, as well as lean cuts of beef, pork, and fish. These protein sources provide essential amino acids necessary for building and repairing muscle tissue, as well as nutrients like iron, zinc, and vitamin B12.
Plant-based lean proteins encompass a diverse range of options, including legumes (such as beans, lentils, and chickpeas), tofu, tempeh, edamame, and certain grains like quinoa. These plant-based proteins are not only rich in protein but also high in dietary fiber, vitamins, minerals, and phytonutrients, making them valuable additions to a balanced diet.
Incorporating lean proteins into meals offers numerous health benefits. Protein is essential for muscle repair and growth, immune function, hormone synthesis, and enzyme production. Additionally, consuming lean proteins can help increase feelings of fullness and satiety, making it easier to manage hunger and maintain a healthy weight.
Choosing lean proteins over higher-fat options can also reduce the intake of saturated fats and cholesterol, which are associated with an increased risk of heart disease and other chronic conditions. By opting for lean proteins, individuals can support heart health and lower their overall risk of cardiovascular disease.
Lean proteins are incredibly versatile and can be prepared using various cooking methods, including grilling, baking, broiling, steaming, and sautéing. They can be incorporated into a wide range of dishes, from salads and stir-fries to soups, sandwiches, and main courses, allowing for endless culinary creativity and flavor exploration.
Whether you prefer animal-based or plant-based options, incorporating lean proteins into your diet is a simple yet effective way to support overall health, maintain muscle mass, and promote satiety. By prioritizing lean proteins and incorporating them into balanced meals, individuals can enjoy the numerous health benefits of these nutrient-rich foods while savoring delicious and satisfying meals.
3.White Rice and Pasta
White rice and pasta are staple ingredients in many cuisines around the world, valued for their versatility, affordability, and comforting texture. While they are often criticized for their high carbohydrate content and lower nutrient density compared to whole grains, white rice and pasta can still be part of a balanced diet when consumed in moderation and paired with nutrient-rich accompaniments.
White rice is a polished grain that has had its bran and germ removed, resulting in a refined product with a softer texture and milder flavor compared to brown or wild rice. Similarly, pasta is made from durum wheat semolina or flour, processed into various shapes and sizes, and cooked by boiling until tender.
Despite their processing, white rice and pasta provide a quick and convenient source of energy due to their high carbohydrate content. They are easily digestible, making them suitable for individuals with sensitive digestive systems or those recovering from illness. Additionally, they serve as blank canvases for a wide range of flavor profiles and culinary creations.
When consumed in moderation and paired with nutrient-dense ingredients such as lean proteins, vegetables, and healthy fats, white rice and pasta can contribute to a balanced meal that satisfies hunger and provides essential nutrients. For example, combining white rice with grilled chicken breast and steamed broccoli creates a well-rounded meal that delivers protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
While white rice and pasta lack the fiber, vitamins, and minerals found in whole grains, they can still be fortified with nutrients such as iron and folic acid to enhance their nutritional value. Additionally, opting for enriched or whole-grain varieties of pasta can provide additional fiber and micronutrients, making them a more nutritious choice.
It’s important to be mindful of portion sizes when consuming white rice and pasta, as overconsumption can lead to spikes in blood sugar levels and contribute to weight gain over time. Balancing these carbohydrate-rich foods with ample servings of vegetables and lean proteins can help slow the absorption of carbohydrates and promote satiety.
4.Ripe Fruits
Ripe fruits are nature’s sweet treasures, bursting with flavor, vibrant colors, and an abundance of nutrients. As fruits ripen, they undergo biochemical changes that result in softening, sweetening, and heightened aroma, making them more appealing and enjoyable to eat. From juicy berries and succulent peaches to fragrant mangoes and plump grapes, ripe fruits offer a delightful sensory experience and a plethora of health benefits.
One of the most noticeable characteristics of ripe fruits is their sweetness. As fruits ripen, their natural sugars, such as fructose, sucrose, and glucose, increase, giving them a pleasant taste that appeals to the palate. This sweetness makes ripe fruits a satisfying and delicious snack option, whether enjoyed on their own or incorporated into a variety of dishes and recipes.
In addition to their sweetness, ripe fruits are also rich in essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. They provide an array of nutrients that support overall health and well-being, including vitamin C, vitamin A, potassium, fiber, and phytonutrients. These nutrients play crucial roles in supporting immune function, promoting healthy digestion, maintaining cardiovascular health, and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
Ripe fruits are also known for their vibrant colors, which are indicative of their nutrient content and antioxidant levels. For example, brightly colored fruits like berries, oranges, and kiwis are rich in antioxidants such as anthocyanins, flavonoids, and vitamin C, which help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals and oxidative stress.
Eating a variety of ripe fruits can provide numerous health benefits and contribute to a well-rounded diet. Incorporating fruits into meals and snacks adds natural sweetness, flavor, and texture while increasing the intake of essential nutrients. Whether enjoyed fresh, blended into smoothies, added to salads, or baked into desserts, ripe fruits offer endless possibilities for delicious and nutritious culinary creations.
Moreover, ripe fruits are versatile ingredients that can be used in both sweet and savory dishes. They can be grilled, roasted, pureed, or preserved to enhance their flavors and textures. Ripe fruits can also be combined with other ingredients to create refreshing beverages, savory sauces, vibrant salads, and decadent desserts, showcasing their culinary versatility and appeal.
5.Yogurt and Fermented Foods
Yogurt and fermented foods are celebrated for their tangy flavors, creamy textures, and numerous health benefits. These probiotic-rich foods undergo a fermentation process that enhances their nutritional profile and introduces beneficial bacteria known as probiotics, which promote gut health and support overall well-being. From traditional yogurt and kefir to sauerkraut, kimchi, and kombucha, fermented foods offer a flavorful and versatile way to incorporate probiotics into your diet.
Yogurt is perhaps the most well-known fermented food, prized for its creamy texture and tart taste. Made by fermenting milk with beneficial bacteria such as Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus, yogurt is rich in probiotics that help maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria. These probiotics support digestion, boost immune function, and may even contribute to weight management and heart health. Additionally, yogurt is a good source of protein, calcium, and other essential nutrients, making it a nutritious addition to meals and snacks.
Kefir is another fermented dairy product similar to yogurt but with a thinner consistency and a slightly tangier flavor. Made by fermenting milk with kefir grains, which contain a variety of beneficial bacteria and yeast strains, kefir offers similar probiotic benefits as yogurt. It is also rich in vitamins, minerals, and amino acids, providing additional nutritional value.
In addition to dairy-based options, a wide variety of plant-based fermented foods are available, offering probiotic benefits to individuals with dietary restrictions or preferences. Sauerkraut, kimchi, miso, tempeh, and kombucha are just a few examples of plant-based fermented foods that provide probiotics and other health-promoting nutrients. These foods are often made by fermenting vegetables, legumes, or grains with beneficial bacteria, resulting in tangy, flavorful products with numerous health benefits.

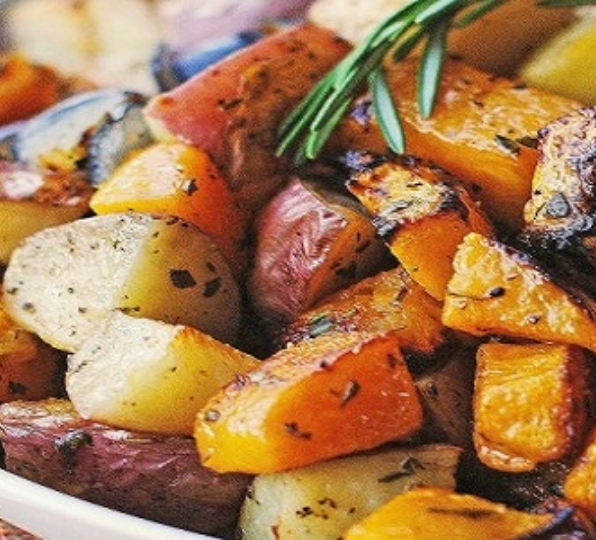
Conclusion:
Choosing foods that are easy to digest is key to supporting digestive health and alleviating discomfort for individuals with sensitive stomachs or digestive issues. Incorporating cooked vegetables, lean proteins, white rice and pasta, ripe fruits, and yogurt and fermented foods into your diet can help promote better digestion and overall well-being. Experiment with different foods and pay attention to how your body responds to find the best options for your individual needs. Remember to listen to your body, eat mindfully, and prioritize a balanced diet for optimal digestive health.












