Introduction:
Breast cancer is one of the most common cancers affecting women worldwide, but it can also occur in men. It develops when cells in the breast grow out of control and form a tumor. While breast cancer can be a serious and potentially life-threatening condition, early detection and advances in treatment have significantly improved survival rates. In this article, we’ll explore what breast cancer is, its causes, symptoms, risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment options, empowering individuals with knowledge to understand and navigate this disease effectively.
1. What is Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the cells of the breast. It can occur in the milk ducts (ductal carcinoma) or the milk-producing glands (lobular carcinoma) of the breast. Over time, cancerous cells can invade surrounding breast tissue and spread to other parts of the body, such as the lymph nodes, bones, liver, or lungs, through a process called metastasis.
2. Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of breast cancer is unknown, but several risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing the disease. These risk factors include:
- Gender: Breast cancer is much more common in women than in men.
- Age: The risk of breast cancer increases with age, with the majority of cases diagnosed in women over 50.
- Family History: A personal or family history of breast cancer or certain genetic mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, can increase the risk.
- Hormonal Factors: Factors such as early menstruation, late menopause, hormone replacement therapy, and never having children or having children later in life can influence breast cancer risk.
- Lifestyle Factors: Obesity, excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, and a sedentary lifestyle may increase the risk of breast cancer.
3.Symptoms
- The most common symptom of breast cancer is a lump or mass in the breast or underarm area. Other signs and symptoms may include:
- Changes in breast size, shape, or appearance
- Nipple changes, such as inversion, discharge, or scaling
- Breast pain or tenderness
- Swelling or redness of the breast or nipple
- Skin changes, such as dimpling, puckering, or thickening
It’s important to note that not all breast lumps are cancerous, but any changes in the breast should be evaluated by a healthcare provider to rule out breast cancer.
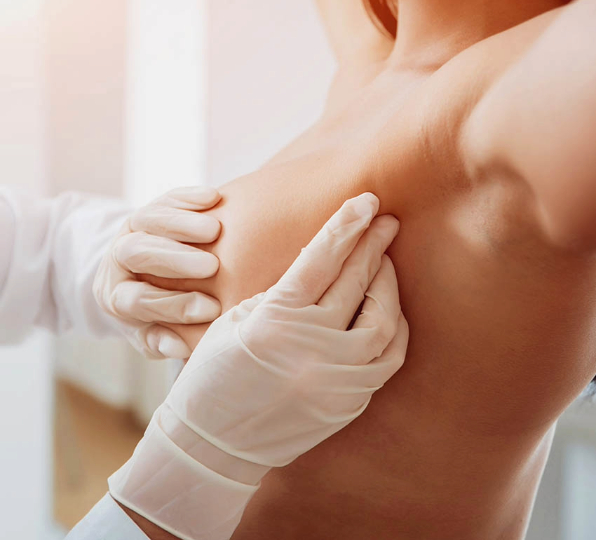
4.Diagnosis
Breast cancer is typically diagnosed through a combination of screening tests and diagnostic procedures. Screening tests such as mammograms, breast ultrasounds, and breast MRIs can detect breast cancer early, often before symptoms develop. If an abnormality is found on a screening test or if symptoms are present, further diagnostic tests such as a breast biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis and determine the extent of the disease.
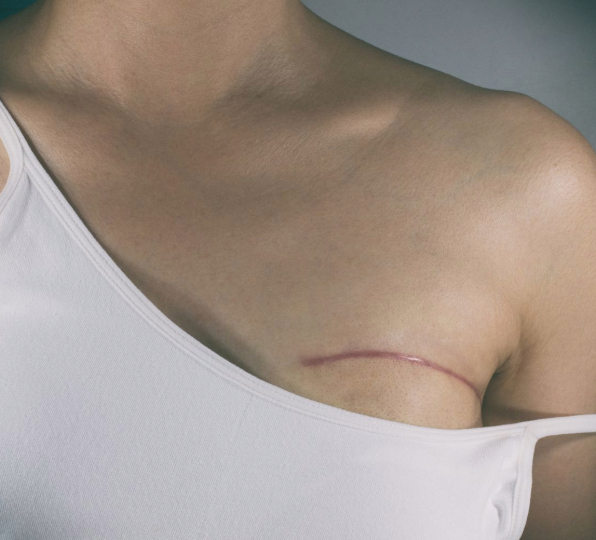
5.Treatment
Treatment for breast cancer depends on various factors, including the type and stage of cancer, as well as the individual’s overall health and preferences. Treatment options may include:
- Surgery: Surgical procedures such as lumpectomy, mastectomy, or lymph node removal may be performed to remove cancerous tissue from the breast.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to target and kill cancer cells in the breast or surrounding tissues.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy involves the use of powerful drugs to kill cancer cells or prevent them from multiplying and spreading.
- Hormone Therapy: Hormone therapy may be used to block the effects of hormones that promote the growth of certain types of breast cancer.
- Targeted Therapy: Targeted therapy drugs target specific molecules or pathways involved in the growth and spread of cancer cells.
Conclusion:
Breast cancer is a complex disease with many factors influencing its development, diagnosis, and treatment. While a breast cancer diagnosis can be frightening, advances in early detection and treatment have significantly improved survival rates and quality of life for individuals with breast cancer. By understanding the causes, symptoms, risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment options for breast cancer, individuals can take an active role in their healthcare and make informed decisions about their breast health. Regular breast self-exams, clinical breast exams, and mammograms are essential for early detection and can help improve outcomes for individuals at risk of breast cancer.